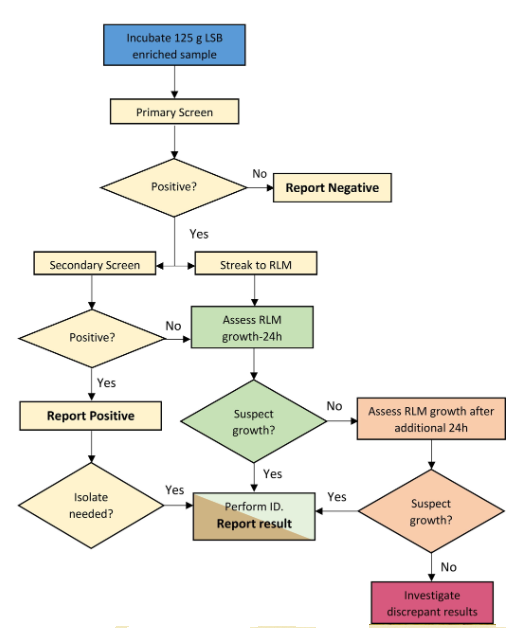
A publication in Food Protection (Vol 87, 1, January 2024) from ConAgra researchers developed a method for cultural confirmation following the detection of Listeria monocytogenes presumptive positive. The alternative method takes 2 days instead of 3-7 days. The alternative confirmation method consisted of two components: (i) a secondary screen using a different rapid method and (ii) concurrent cultural isolation followed by next-day colony identification. Four food matrices (hot dogs, peanut butter, frozen vegetables, and multi-component frozen meals) were inoculated with low levels (0.36–1.39 MPN/125 g) of L. monocytogenes. Analyses started with a PCR primary screen (Bio-Rad iQ-Check Listeria monocytogenes II). Enriched food samples underwent a secondary screen by bioMérieux’s GENE-UP LMO2 Real-Time PCR, VIDAS LMX ELFA, and streaking onto RAPID’L.mono Agar. Presumptive positive L. monocytogenes colonies were identified utilizing a high throughput rapid identification method (Hygiena’s BAX SystemL. Monocytogenes Real-Time PCR assay, Neogen’s ANSR isothermal nucleic acid amplification assay, and Bruker’s MALDI Biotyper). Overall, there was no statistically significant difference (p ≤ 0.05) between the number of L. monocytogenes-positive obtained by the cultural reference method and the alternative confirmation methods (regardless of which method combinations were evaluated). Additionally, this study supports that when the primary and secondary screen methods yield a positive result, the sample could be considered a confirmed positive for L. monocytogenes. @ https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0362028X23068771
Rapid confirmation method for identifying Listeria monocytogenes from 125 g food samples within two days of a PCR presumptive positive
No comments