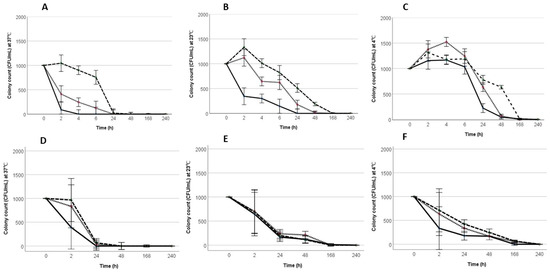
A study published in Pathogens (2019, 8(4), 218) describes the work of a research team from Flinders University in Adelaide, Australia, that developed a method to remove Salmonella Typhimurium (ST) from eggshells without effecting the egg’s usability and quality. The research investigated the effect of pH and temperature on the survival of Salmonella Typhimurium (ST) in peptone water (PW) and mayonnaise. The pH of PW and mayonnaise was adjusted to 4.2, 4.4, and 4.6 using acetic acid and vinegar, respectively. The PW and mayonnaise were inoculated with ST and incubated at 37 °C, 23 °C, and 4 °C. The survival of Salmonella was determined using the drop plate method. Survival was significantly (p < 0.05) improved at 4 °C. In both mayonnaise and PW, following 24 h, there was no ST growth at pH 4.2. Resuscitation of ST was rapidly observed at 4 °C, while complete inactivation was observed at 37 °C at pH 4.2, 4.4, and 4.6 in both PW and mayonnaise. Lower temperatures protected ST from the bactericidal effect of low pH. This study showed that lower temperatures reduce the antibacterial activity of the organic acids, which allowed Salmonella to survive at low pH for longer. Preparing home-made mayonnaise at pH 4.2 and retaining at room temperature for at least 24 h effectively killed S. Typhimurium and could aid in reducing the prevalence of the salmonellosis outbreaks in Australia. Results of this study indicate that the combined effect of pH 4.2 and the incubation temperature, 37 °C was the most effective at reducing S. Typhimurium; however, incubating at 23 °C was still more effective than 4 °C and may present a more practical approach. @ https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0817/8/4/218/htm