Publix Super Markets Inc. recalled Biltmore smoked salmon due to the risk of Listeria monocytogenes contamination. Seven Seas International LLC USA of St. Petersburg, FL, supplied Publix with the sockeye salmon. The Listeria problem “was discovered through routine regulatory testing conducted by the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services,” according to the recall notice. As of May 12, the recall notice had not been posted by the Food and Drug Administration. @ http://stopfoodborneillness.org/05-13-2019/
ruth
http://stopfoodborneillness.org/05-13-2019/
ruth
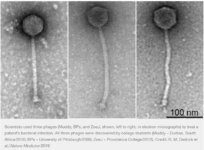
Scientists (Rebekah M. Dedrick et al. “Engineered bacteriophage for treatment of a patient with a disseminated drug-resistant Mycobacterium abscessus.” Nature Medicine. May 8, 2019), used an experimental phage therapy (https://www.hhmi.org/news/phage-therapy-treats-patient-with-drug-resistant-bacterial-infection) to save a 15-year-old girl infected with drug-resistant Mycobacterium
The patient had cystic fibrosis, and for eight years, she had been taking antibiotics to control two stubborn Mycobacterium abscessus strains. After the transplant, the girl’s infection had spread, and traditional antibiotics were no longer working. A specialized treatment based on genetically engineered bacteriophages was developed. After an extensive search, the team found a combination of 3 phages. After removing a gene that lets the phages reproduce harmlessly within a bacterial cell, the phages reproduce and burst from the cell, destroying it. Then they combined the trio into a phage cocktail, purified it, and tested it for safety. The doctors administered the cocktail to the patient via an IV twice daily with a billion phage particles in every dose. As a result of the treatment, the patient got better.
Scientists have used an experimental therapy that relies on bacteria-infecting viruses collected, in part, through HHMI’s SEA-PHAGES program to fight a Mycobacterium infection in a 15-year-old girl.
ruth
The FDA announced that Mecox Bay Dairy, LLC, recalled Mecox Sunrise washed-rind Tomme style cheese because it has the potential to be contaminated with Listeria monocytogenes. The cheese was distributed and sold at seven retail locations and one restaurant on Eastern Long Island, NY, and served at one restaurant in Chicago, IL. The product comes in a clear plastic package marked with “Mecox Sunrise” cheese label. As of the date of this release, all affected Mecox Sunrise has been removed from all stores and restaurants. No illnesses have been reported to date in connection with this product. The potential for contamination was noted after routine testing by New York State Agriculture and Markets Division of Milk Control revealed the presence of Listeria monocytogenes in a sample of Mecox Sunrise cheese. @ https://www.fda.gov/safety/recalls-market-withdrawals-safety-alerts/mecox-bay-dairy-llc-recalls-mecox-sunrise-cheese-because-possible-health-risk?utm_campaign=Mecox%20Bay%20Dairy%2C%20LLC%20Recalls%20%E2%80%9CMecox%20Sunrise%E2%80%9D%20Cheese%20Because%20of%20Possible%20Health%20Risk&utm_medium=email&utm_source=Eloqua
https://www.fda.gov/safety/recalls-market-withdrawals-safety-alerts/mecox-bay-dairy-llc-recalls-mecox-sunrise-cheese-because-possible-health-risk?utm_campaign=Mecox%20Bay%20Dairy%2C%20LLC%20Recalls%20%E2%80%9CMecox%20Sunrise%E2%80%9D%20Cheese%20Because%20of%20Possible%20Health%20Risk&utm_medium=email&utm_source=Eloqua
ruth
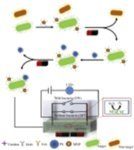
Hou et al. from China Agricultural University published in Food Control (A microfluidic signal-off biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella using magnetic separation and enzymatic catalysis @ https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0956713519301550?dgcid=rss_sd_all Food Control 2019, 103: 186-193.) about a rapid and sensitive method for the detection of Salmonella typhimurium using a microfluidic biosensor containing magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) with catalases. Catalases, are common enzymes found in all living organisms and were used in the biosensor to amplify the biological signal greatly. The MNPs was modified with anti-Salmonella monoclonal antibodies and used to separate and enrich Salmonella from sample background flora. The Salmonella was further reacted with polystyrene microspheres (PSs) modified with anti-Salmonella polyclonal antibodies and catalases. Then, the conjugated bacteria were injected into the capillary in a microfluidic chip and captured by high gradient magnetic field. After washing to remove unbound PSs, hydrogen peroxide was finally injected and catalyzed by the catalases on enzymatic bacteria to produce oxygen gaps in the capillary, leading to an electrical signal. A linear relationship was found between the change of electrical voltage and the concentration of target bacteria from 3.7 × 101 to 3.7 × 106 CFU/mL. The biosensor was able to detect Salmonella as low as 33 CFU/mL within 2 h, and could be further combined with microfluidic to develop a lab-on-a-chip system. In testing using salmonella-spiked milk, the mean recovery was 104.7%.
The key to prevent and control the spread of foodborne diseases is rapid screening and early warning of pathogenic bacteria in foods. In this study, a…