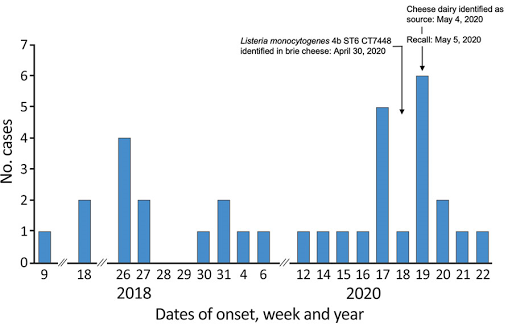
An article (Nüesch-Inderbinen et al. Listeriosis Caused by Persistence of Listeria monocytogenes Serotype 4b Sequence Type 6 in Cheese Production Environment. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021;27(1):284-288) describes a nationwide outbreak of human listeriosis in Switzerland that was traced to persisting environmental contamination of a dairy with Listeria monocytogenes . Whole-genome sequencing identified L. monocytogenes serotype 4b, sequence type 6, cluster type 7488, in the environment. The prolonged outbreak of L. monocytogenes caused 34 laboratory-confirmed listeriosis cases and ten deaths. The investigation results implicated a dairy with sanitation shortcomings and persisting environmental contamination throughout the production site. Isolation and WGS typing of L. monocytogenes from a quality-control cheese sample provided crucial information that enabled identifying the contamination origin. WGS played a crucial role in showing close relatedness between the isolates from the cheese item and the environment and linking the listeriosis cases from 2018 to the 2020 outbreak. The outbreak highlights the risk for recontamination of pasteurized cheese products during manufacturing and emphasizes the need for a routine sampling of products, manufacturing equipment, and the production environment. @ https://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid2701.203266
Listeriosis caused by persistence of Listeria monocytogenes in cheese production environment
Listeriosis Caused by Persistence of Listeria monocytogenes Serotype 4b Sequence Type 6 in Cheese Production Environment
A nationwide outbreak of human listeriosis in Switzerland was traced to persisting environmental contamination of a cheese dairy with Listeria monocy…
No comments