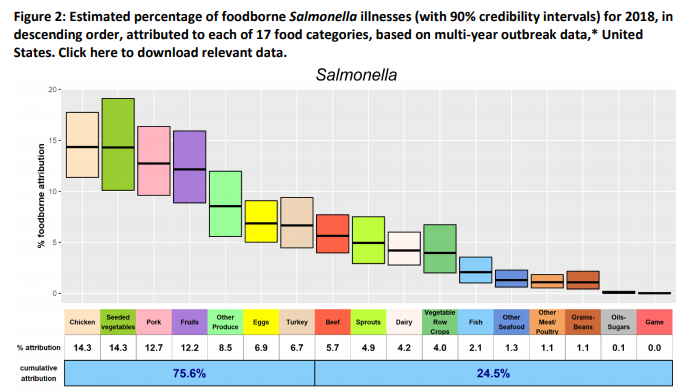
The Interagency Food Safety Analytics Collaboration (IFSAC) is a tri-agency group created by the CDC, the FDA, and the USDA-FSIS. IFSAC developed a method to estimate the percentages of foodborne illness attributed to specific sources using outbreak data from 1998 through the most recent year for four priority pathogens: Salmonella, Escherichia coli O157, Listeria monocytogenes, and Campylobacter. Each year in the US, an estimated 9 million people get sick, 56,000 are hospitalized, and 1,300 dies of foodborne disease caused by food pathogens. More than 75% of Salmonella illnesses were attributed to seven food categories: Chicken, Seeded Vegetables (such as tomatoes), Pork, Fruits, Other Produce (such as nuts), Eggs, and Turkey. Over 75% of E. coli O157 illnesses were linked to Vegetable Row Crops (such as leafy greens) and Beef. More than 75% of Listeria monocytogenes illnesses were attributed to Dairy products and Fruits. Over 75% of non-Dairy Campylobacter illnesses were linked to Chicken. @ https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/ifsac/annual-reports.html
Foodborne illness source estimates for 2018 for Salmonella, Escherichia coli O157, Listeria monocytogenes, and Campylobacter
Annual Reports on Foodborne Illness Source Attribution Estimates | Interagency Food Safety Analytics Collaboration | Food Safety | CDC
No comments