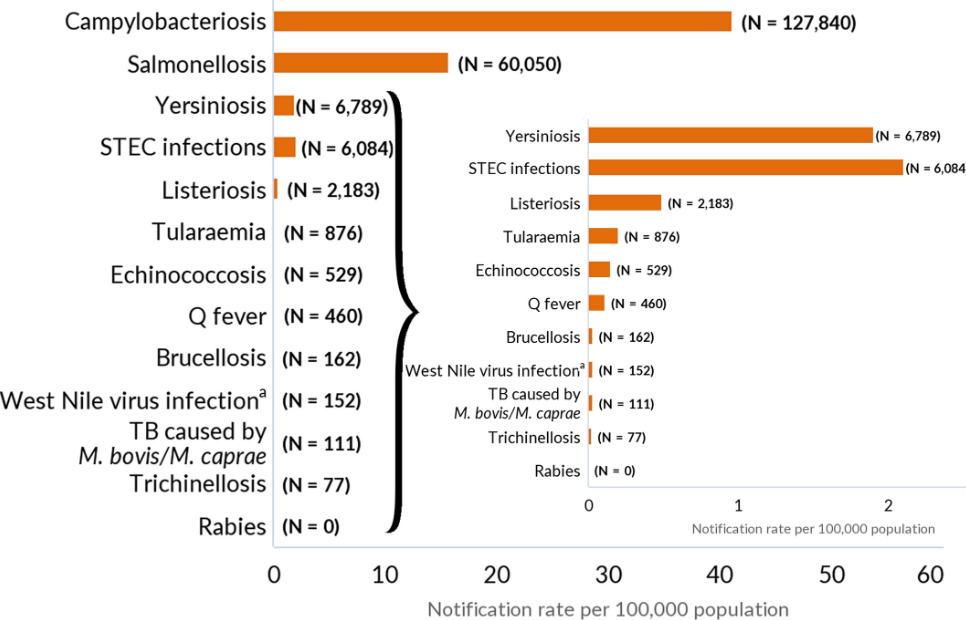
The report of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) presents the results of zoonoses monitoring and surveillance activities carried out in 2021 in 27 MSs, the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) and nine non MSs. Countries. Zoonoses are illnesses that can be spread between animals and people. Overall, MSs reported more foodborne outbreaks and cases in 2021 than 2020. In 2021, the first and second most reported human zoonoses were campylobacteriosis and salmonellosis, respectively. Cases of campylobacteriosis and salmonellosis increased compared to 2020 but decreased compared with previous years. In 2021, data collection and analysis at the EU level were still impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic and the control measures adopted in the MSs. Salmonella samples from carcasses of various animal species and samples for Campylobacter quantification from broiler carcasses were more frequently positive when performed by the competent authorities than when own-checks were conducted. Yersiniosis was the third most reported zoonosis in humans, followed by Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and Listeria monocytogenes infections. L. monocytogenes and West Nile virus infections were the most severe zoonotic diseases, with the most hospitalizations and highest case fatality rates. S. Enteritidis remained the most frequently reported causative agent for foodborne outbreaks. Outbreaks linked to ‘vegetables and juices and their products rose considerably compared with previous years.@ https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.2903/j.efsa.2022.7666