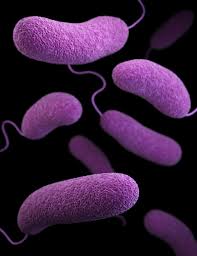
A study published in Emerging Infectious Disease (26, 2) reports that compared with other major foodborne illnesses, Vibrio parahaemolyticus infections have been steadily increasing. The CDC estimated that the average annual incidence of all Vibrio infections increased by 54% during 2006–2017. V. parahaemolyticus is believed to be responsible for ≈35,000 human infections each year in the United States alone. Since the 1990s, it has been identified as a leading cause of foodborne infections in China. ST36 infections were reported in the northeastern United States in 2012. Later, they were reported in a single large outbreak in Spain. The ST36 is a highly dynamic population and that the V. parahaemolyticus strains to cause infections in the northeastern United States had diverged from the original lineage in the Pacific Northwest throughout the cross-continent eastward expansion. The study reports a transcontinental expansion of ST36 V. parahaemolyticus into South America. International trade of shellfish might be involved in the dispersal of Vibrio parahaemolyticus populations into the United States and Spain. The study found that severe weather, such as El Niño conditions in Peru, provide ideal conditions for the proliferation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. ST36’s ability for intercontinental dispersal, along with its highly pathogenic nature, makes this Vibrio population a major public health concern. Peru has shown that implementation of systematic surveillance for Vibrio species can facilitate the detection of emerging transnational epidemic strains. @ https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/26/2/19-0362_article
CDC reports global expansion of Pacific Northwest Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Global Expansion of Pacific Northwest Vibrio parahaemolyticus Sequence Type 36
We report transcontinental expansion of Vibrio parahaemolyticus sequence type 36 into Lima, Peru. From national collections, we identified 7 isolates …
No comments