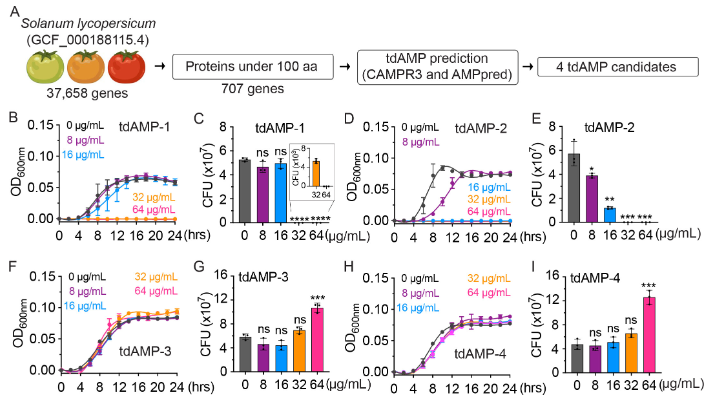
Know et al. published in Microbiology Spectrum (Volume 12, issue 1, 2024) an article entitled Antimicrobial properties of tomato juice and peptides against typhoidal Salmonella. Tomatoes' antimicrobial properties remain largely unexplored. The authors presented the findings on the antimicrobial properties of tomato juice and peptides, namely, tomato-derived antimicrobial peptides (tdAMPs) and their effectiveness against typhoidal Salmonella. The study has revealed that tomato juice demonstrates significant antimicrobial properties against Salmonella Typhi. By conducting computational analysis of the tomato genome sequence, conducting molecular dynamics simulation, and performing functional analyses, they successfully identified two tdAMPs, namely, tdAMP-1 and tdAMP-2. These tdAMPs have demonstrated potent antimicrobial properties by effectively disrupting bacterial membranes. The efficacy of tdAMP-2 is shown to be more effective than tdAMP-1. The efficacy of tdAMP-1 and tdAMP-2 has been demonstrated against drug-resistant S. Typhi and hyper-capsular S. Typhi variants that possess hypervirulent characteristics, which are presently circulating in countries with endemicity. Tomato juice and the two tdAMPs have also demonstrated effectiveness against uropathogenic Escherichia coli, showing their potential as viable agents in combating certain Gram-negative pathogens. This study provides valuable insights into the development of effective and sustainable public health strategies that utilize tomatoes and their derivatives as lifestyle interventions.@ https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/spectrum.03102-23