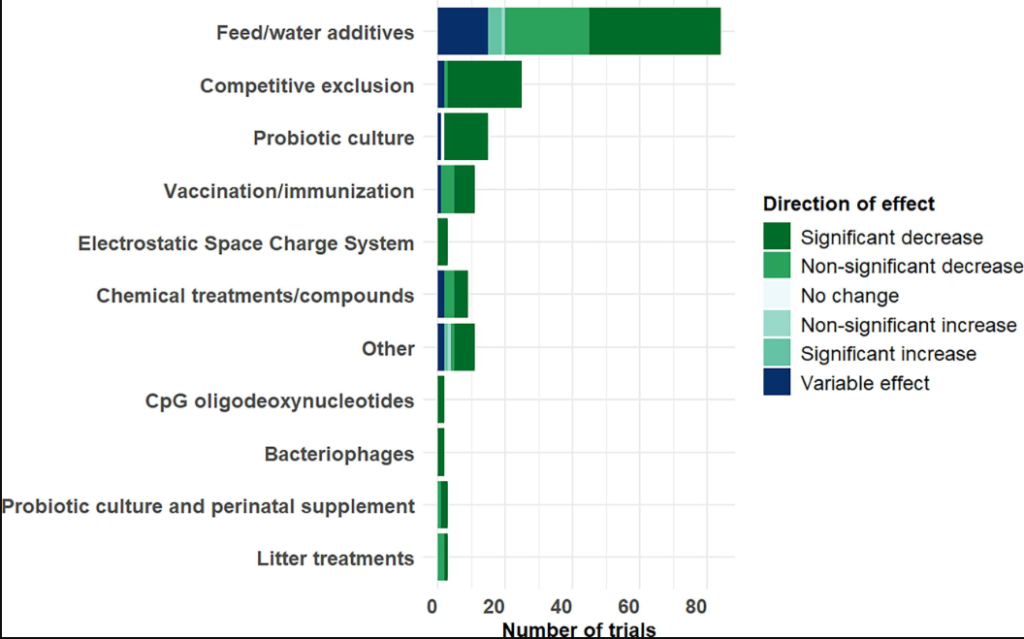
An article in J Food Protection entitled “A Systematic Review on Preharvest Interventions Used to Control Salmonella in Poultry Rearing in the United States” was published on 27 February 2025. Feed/water additives were most frequently studied as preharvest Salmonella controls. Currently, there is no systematic literature review of preharvest interventions that control Salmonella in poultry in the US. A literature search was conducted. Experimental studies published from 1995 to 2022 assessing preharvest interventions to control Salmonella in US poultry farms. A total of 12,403 publications were identified, and 234 publications were included in the final review. The most evaluated interventions were feed/water additives (51.50%), competitive exclusion culture (10.30%), vaccination/immunization (7.88%), chemical treatments/compounds (5.45%), and probiotic culture (4.85%). Most studies focused on broiler chicken (78.20%) compared to turkey and investigated Salmonella Typhimurium (37.60%), S. Enteritidis (29.10%), and S. Heidelberg (8.48%). This review improves our understanding of the breadth of preharvest interventions and their effectiveness against Salmonella in poultry. It can also be used to inform food safety policies and practices around poultry to protect public health. @ https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0362028X25000262?via%3Dihub