Scientists at Vetmeduni Vienna University published in the International Journal of Food Microbiology (Vol 328, 2 September 2020), their research about the microbial composition of biofilms within a meat processing environment, processing pork, poultry, and beef, by the detection of microorganisms and biofilm matrix components. Sampling included 47 food contact surfaces and 61 non-food contact surfaces from eleven rooms within an Austrian meat processing plant, either during operation or after cleaning and disinfection. The 108 samples were analyzed for the presence of microorganisms by cultivation and targeted quantitative real-time PCR based on 16S rRNA. Ten hotspots were identified, five on food contact surfaces such as cutting machines and accessories. Seven of the biofilm-positive samples were taken during operation and three after cleaning and disinfection, including one at a screw conveyor. Biofilms are found on 9.3% sites, and a range of bacteria from 29 different types were found. Cultivated bacteria from these sites identified Brochothrix (present in 80 % of biofilms), and Pseudomonas, and Psychrobacter (isolated from 70 % biofilms). The study found biofilms in drains and water hoses as critical sources of contamination. @ https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168160520301628
ruth
Biofilms are comprised of microorganisms embedded in a self-produced matrix that normally adhere to a surface. In the food processing environment theyâ¦
ruth
Stephen Hahn, Commissioner of Food and Drugs in the Food and Drug Administration, released details about the new era of food safety. Traceability, in minutes not days, is critically important in outbreak investigation. FDA wants to encourage food companies to adopt tracing technologies and to harmonize these efforts. This will allow the FDA to spot potential problems in advance and help us prevent or lessen their impact. The FDA intends to conduct more meaningful and predictive data analysis that is strategic and prevention-oriented. The FDA is conducting a pilot program that will leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to strengthen the agency’s review of imported foods. To ensure food safety FDA intends to continue oversight as technology evolves. @ https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-launches-new-era-smarter-food-safety-initiative-releases-blueprint-and-pilot-study?utm_campaign=071320_PR_FDA%20Launches%20New%20Era%20of%20SFSI%2C%20Releases%20Blue%20Print%20and%20Pilot%20Study&utm_medium=email&utm_source=Eloqua
FDA Launches New Era of Smarter Food Safety Initiative, Releases Blueprint and Pilot Study
ruth
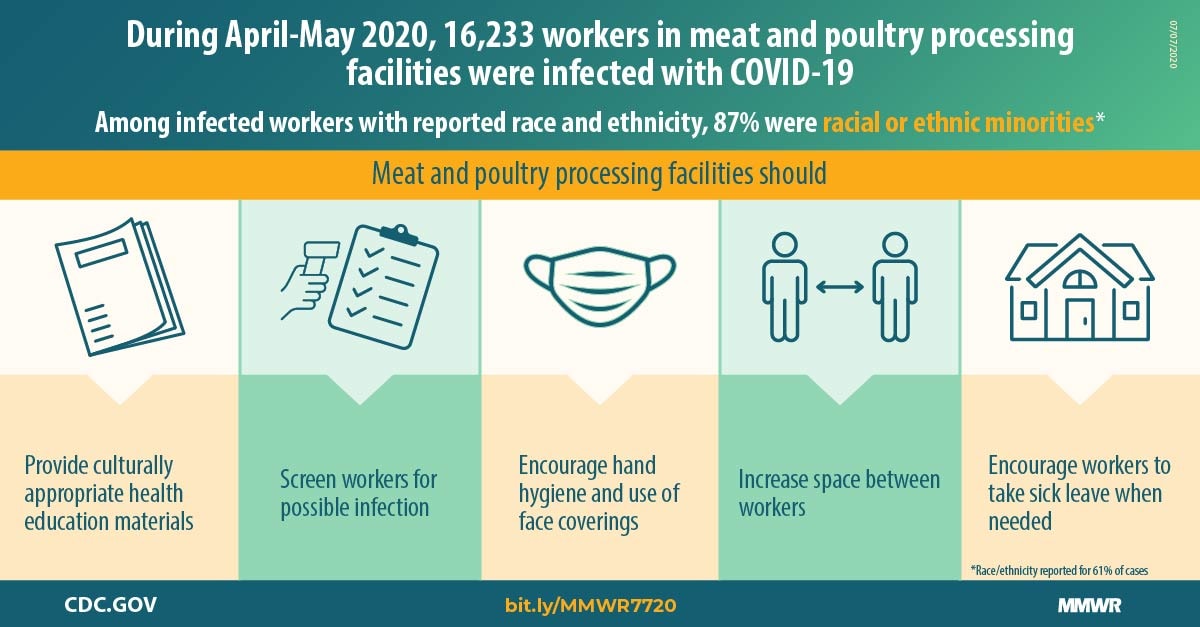
Morbidity and mortality reports that among 23 states reporting COVID-19 outbreaks in meat and poultry processing facilities, 16,233 cases in 239 facilities occurred, including 86 (0.5%) COVID related deaths. Among 14 states reporting the total number of workers in affected meat and poultry processing facilities (112,616), COVID-19 was diagnosed in 9.1% of workers. Among 9,919 (61%) cases in 21 states with reported race/ethnicity, 87% occurred among racial and ethnic minority workers. Commonly reported interventions and prevention efforts at facilities included implementing worker temperature or symptom screening and COVID-19 education, mandating face coverings, adding hand hygiene stations, and adding physical barriers between workers. The proportion of asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic infections among meat and poultry processing workers was 11.2%. High population-density workplace settings such as meat and poultry processing facilities present ongoing challenges to preventing and reducing the risk for COVID transmission. @ https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/69/wr/mm6927e2.htm
Meat and poultry processing facilities face distinctive challenges in the control of infectious diseases, including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) (1). COVID-19 outbreaks among meat and poultry..
ruth
Tyson Foods currently relies on about 122K workers to produce about 20% of chicken, beef, and pork produced in the U.S. Due to the coronavirus pandemic Tyson is pushing further into robotics, developing an automated deboning system destined to handle some of the roughly 39M chickens it processes each week. Pilgrim’s Pride the second-largest U.S. chicken processor, deboning machines now trail humans by only 1% – 1.5%, in terms of meat yield per chicken. “Everybody’s thinking about automation, and it’s going to increase,” said Decker Walker, a managing director with Boston Consulting Group, who works with meatpackers. @ https://seekingalpha.com/amp/news/3590102-pandemic-meatpackers-thinking-automation