The Australian Competition & Consumer Commission (“ACCC”) reports that JB Nicholas and Son (Geeveston, Tasmania) recalls Premium Tasmanian Smoked Ham Meat products from the Australian marketplace due to suspected Listeria monocytogenes contamination. The recalled product is Premium Tasmanian Smoked Ham Meat products, packaged in 250 gram vacuum bags with a use-by date code of 16OCT21. The products were marketed, distributed, and sold in the Australian states of Tasmania and Victoria. The product has been available for sale at Hill Street Grocer Sandy Bay, Geeveston, Cygnet IGAs in TAS, and independent food retailers, including IGA in VIC. @ https://www.productsafety.gov.au/recalls/jb-nicholas-and-son-%E2%80%94-premium-tasmanian-smoked-ham-250g
ruth
ruth
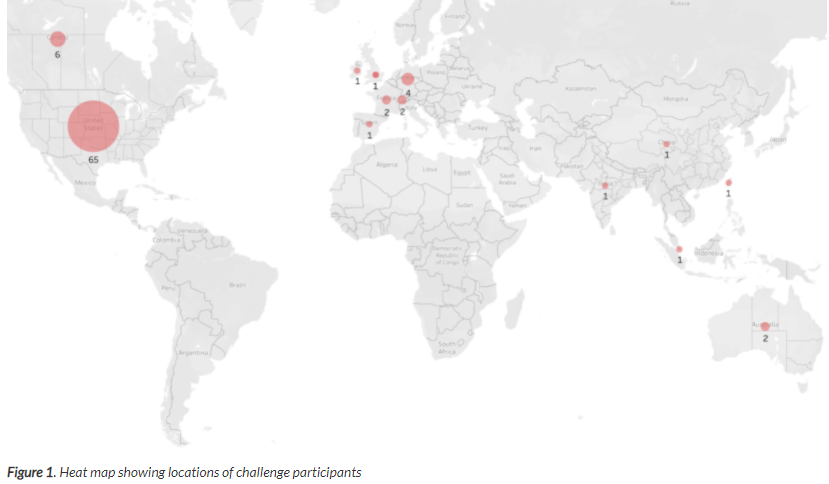
FDA announces the 12 winners of the FDA New Era of Smarter Food Safety Low- or No-Cost Tech-Enabled Traceability Challenge. There were 90 submissions, with the winning teams representing the U.S., Canada, and New Zealand. There were 90 submissions received with teams from Australia, China, England, France, Germany, India, Ireland, Singapore, Spain, Switzerland, and Taiwan. A goal of the FDA’s initiative is to help achieve end-to-end. The primary goal of this challenge has been to encourage stakeholders, including technology providers, public health advocates, entrepreneurs, and innovators from all disciplines to develop traceability hardware, software, or data analytics platforms that are low-cost or no-cost to the end-user. @ https://precision.fda.gov/challenges/13/results?utm_medium=email&utm_source=govdelivery
A community for NGS assay evaluation
ruth
The FDA reported that Dole Fresh Vegetables, Inc recalled a limited number of conventional Curly Leaf Parsley cases. The product being recalled is Dole® Curly Leaf Parsley, with harvest dates of August 18, 2021, and August 19, 2021. A random, routine regulatory sample collected in Michigan tested positive for non-O157 STEC. No illnesses have been reported. The product was distributed to retail stores, wholesalers, and distributors in two pack sizes – 60-count (74 cases) and 30-count (39 cases). The Curly Leaf Parsley subject to this recall was distributed in FL, IA, MI, MN, and MO. This precautionary recall is initiated due to a positive non-O157 STEC result found on a single sample collected by the Michigan Department of Agriculture during routine random sampling. @ https://www.fda.gov/safety/recalls-market-withdrawals-safety-alerts/dole-fresh-vegetables-announces-precautionary-limited-recall-curly-leaf-parsley-due-possible
Dole Fresh Vegetables, Inc. is voluntarily recalling a limited number of cases of conventional Curly Leaf Parsley. The product being recalled is Dole® Curly Leaf Parsley, with harvest dates of August 18, 2021, and August 19, 2021. A random, routine regulatory sample collected in Michigan tested po
ruth
In July 2021, CDC, public health, and regulatory officials in several states and the USDA-FSIS began investigating a multistate outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes infections. Epidemiologic, laboratory, and traceback data showed that frozen, fully cooked chicken products supplied by Tyson Foods Inc. were the cause. On July 3, 2021, Tyson Foods Inc recalled approximately 8,955,296 pounds of ready-to-eat chicken products. Additional products made with Tyson Foods Inc. chicken were recalled on July 8 and July 13, 2021. As of September 10, 2021, this outbreak is over. Three people infected with the outbreak strain of Listeria monocytogenes were reported from two states. All three people were in a long-term care facility or hospital when they got sick. WGS showed that bacteria from sick people’s samples were identical, suggesting that people in this outbreak got sick from the same food. USDA-FSIS found the outbreak strain of Listeria in two samples of fully cooked chicken products during routine product testing. USDA-FSIS and partners collected food purchase records from the long-term care facility and hospital to determine the source of the fully cooked chicken products served. USDA-FSIS found that the Tyson facility in Dexter, Missouri, produced one of the products that tested positive for the outbreak strain. The product was supplied to another firm. From this firm, a positive sample was collected. The product was distributed to the long-term care facility and the hospital. @ https://www.cdc.gov/listeria/outbreaks/precooked-chicken-07-21/details.html
Read investigation details about a Listeria outbreak linked to fully cooked chicken.