The VITAL project combines lab-on-chip rapid method and Artificial Intelligence for the rapid method validation
By Pedro Jesús Lopez, AI TALENTUM, Spain
 Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a revolutionary tool bursting into several fields, offering notable advantages such as speed, accuracy, a recommendation of actions, and faster decisions. Microbiology is a field in which AI could be beneficial, and currently, there are some AI projects under development. One of these innovative projects was presented in the IAFP webinar (Validation of Innovative Tools to Assess and improve Microbial safety in the Food Chain) is the VITAL Project. The project relies on a combination of two of the most cutting-edge innovations: lab-on-chip rapid method and AI. It is a food safety related-project, focused on the search of a personalized validation scheme for a lab-on-chip rapid method for Salmonella detection by using AI. The “personalized validation scheme” means the optimized number of samples required for validation depending on the rapid method capabilities (summarized in the validation results of statistical quantities), the food scope studied, the enrichment applied, etc.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a revolutionary tool bursting into several fields, offering notable advantages such as speed, accuracy, a recommendation of actions, and faster decisions. Microbiology is a field in which AI could be beneficial, and currently, there are some AI projects under development. One of these innovative projects was presented in the IAFP webinar (Validation of Innovative Tools to Assess and improve Microbial safety in the Food Chain) is the VITAL Project. The project relies on a combination of two of the most cutting-edge innovations: lab-on-chip rapid method and AI. It is a food safety related-project, focused on the search of a personalized validation scheme for a lab-on-chip rapid method for Salmonella detection by using AI. The “personalized validation scheme” means the optimized number of samples required for validation depending on the rapid method capabilities (summarized in the validation results of statistical quantities), the food scope studied, the enrichment applied, etc.
The use of a rapid method such as lab-on-chip rapid method arises from the necessity to speed up the detection of Salmonella in the raw materials received by processing plants. Fast detection of food contamination using a rapid method means rapid feedback that could be translated into saving a considerable amount of food waste.
One of the drawbacks of adopting a new method is the need to validate such a technique. The validation of rapid methods could be costly, complicated, and time-consuming. AI and statistics could be applied to reduce the number of samples that need to be analyzed during the validation process, but still, comply with the conditions required by the ISO 16140. In this way, it would allow manufacturers to validate the efficacy and accuracy of the rapid methods in actual factory conditions faster and cheaper.
VITAL is an artificial intelligence system created by a Spanish start-up AI TALENTUM, collaborating with the University of Turin and companies such as SwissDecode and sponsored by the EIT Food consortium. This project aims to define an AI-personalized scheme for a new upcoming lab-on-chip rapid methods validation. This protocol could replace the required conditions by the ISO by offering a new statistically-optimized number of samples to test, allowing speeding up of the production while maintaining food security. Simpler validation of rapid methods will result in faster and more often adaptation. The flow diagram below shows the AI process adopted by VITAL.
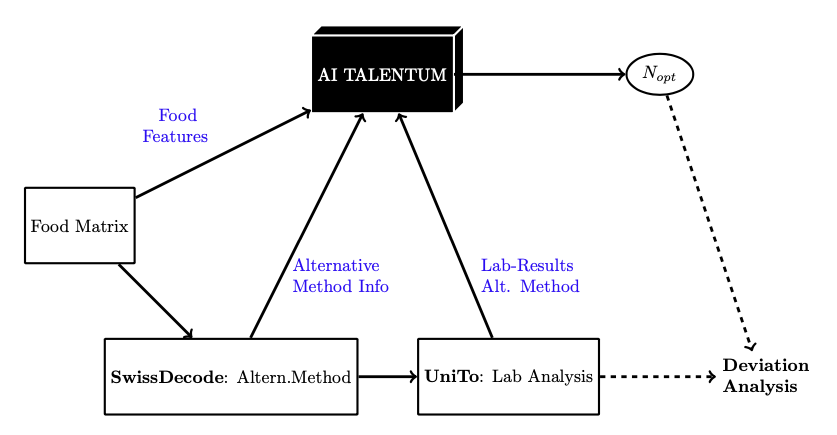
A database composed of data from the certification reports from several rapid methods has been analyzed to achieve a smarter validation. Among the data considered there is information about the validation results (in terms of statistical quantities such as sensitivity, False Positive Rate (FPR), False Negative Rate (FNR), etc.) as well as information from the enrichment step and the features of the analyzed food (pH, water activity, salt content). The validation data of other rapid methods were used to develop an algorithm that is capable of rapidly providing an optimized procedure. The algorithm uses statistical analysis to define a new validation scheme in a few seconds with an optimized number of samples to test that ensures the statistical significance. The validation reports contain information about 1) Samples distribution 2) Enrichment 3) validation results. On the other hand, we have created a database of food features.
It might be possible to reduce the number of samples from the 25-samples established by the ISO to 15-20 to keep an adequate statistical significance. When a new rapid method arrives to be analyzed, the AI system will be executed, taking as inputs the results of the validation of the rapid method in the certification lab. It will analyze for a particular food category the optimized number of samples in a few seconds. The comparison of the rapid new method vs. reference method is implicit in the validation results, which is the crucial aspect of the database.
The VITAL algorithm will be ready by the end of the year. It is a personalized algorithm for the current validation data studied from the companies involved in the project. Still, it could be customized to other data from other sets of validation methods. Therefore, it is a promising tool that could be scalable and moved into other companies.
For more information please contact Antonio Vicente Contreras, AI Talentum CEO, (https://es.linkedin.com/in/antonio-vicente-contreras-2727aa25)
